Importance of Terminal Amino Acid Residues to the Transport of Oligopeptides across the Caco-2 Cell
- Liven Qian

- Nov 12, 2018
- 2 min read
Importance of Terminal Amino Acid Residues to the Transport of Oligopeptides across the Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
文献作者:Long Ding, Liying Wang, Zhipeng Yu, Sitong Ma, Zhiyang Du, Ting Zhang, and Jingbo Liu 《JOURNAL OF AGRICULTURAL AND FOOD CHEMISTRY》
ABSTRACTS
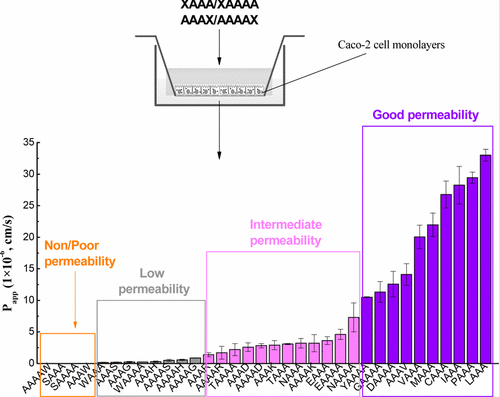
The objective of this paper was to investigate the effects of terminal amino acids on the transport of oligopeptides across the Caco-2 cell monolayer. Ala-based tetra- and pentapeptides were designed, and the N- or C-terminal amino acid residues were replaced by different amino acids. The results showed that the oligopeptides had a wide range of transport permeability across the Caco-2 cell monolayer and could be divided into four categories: non-/poor permeability, low permeability, intermediate permeability, and good permeability. Tetrapeptides with N-terminal Leu, Pro, Ile, Cys, Met, and Val or C-terminal Val showed the highest permeability, with apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) values over 10 × 10–6 cm/s (p < 0.05), suggesting that nonpolar hydrophobic aliphatic amino acids or polar sulfur-containing amino acids were the best for the transport of tetrapeptides. Pentapeptides with N- or C-terminal Tyr also showed high permeability levels, with Papp values of about 10 × 10–6 cm/s. The amino acids Glu, Asn, and Thr at the N terminus or Lys, Asp, and Arg at the C terminus were also beneficial for the transport of tetra- and pentapeptides, with Papp values ranging from 1 × 10–6 to 10 × 10–6 cm/s. In addition, peptides with amino acids replaced at the N terminus generally showed higher permeability than those with amino acids replaced at the C terminus (p < 0.05), suggesting that N-terminal amino acids were more important for the transport of oligopeptides across the Caco-2 cell monolayer.
KEY WORDS
amino acid; brush border membrane peptidase; Caco-2 cell monolayer; oligopeptide; transport permeability
SCREENSHOT

RELATED PRODUCTS
All peptides were synthesized by solid-phase procedures using Fmoc-protected amino acid synthetic methods with purity over 95% by ChinaPeptide Co., Ltd.
CHAINING
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03450






Comments